Similar to any other testing that lies under Independent
Verification and Validation, ETL also go through the same phase.
-Business and requirement understanding
-Validating
-Test Estimation
-Test planning based
on the inputs from test estimation and business requirement
-Designing test cases and
test scenarios from all the available inputs
-Once all the test cases are ready
and are approved, testing team proceed to perform pre--execution check
and test data preparation for
testing
-Lastly execution is performed till
exit criteria are met
-Upon successful completion summary
report is prepared and closure process is done.
It is necessary to define test
strategy which should be mutually accepted by stakeholders before starting
actual testing. A well-defined test strategy will make sure that correct
approach has been followed meeting the testing aspiration. ETL testing might
require writing SQL statements extensively by testing team or may be tailoring
the SQL provided by development team. In any case testing team must be aware of
the results they are trying to get using those SQL statements.
There is a popular misunderstanding that database testing and data warehouse is
similar while the fact is that both hold different direction in testing.
Database testing is done using
smaller scale of data normally with OLTP (Online transaction processing) type
of databases while data warehouse testing is done with large volume with data
involving OLAP (online analytical processing) databases.
In database testing normally
data is consistently injected from uniform sources while in data warehouse
testing most of the data comes from different kind of data sources which are
sequentially inconsistent.
We generally perform only CRUD
(Create, read, update and delete) operation in database testing while in data
warehouse testing we use read-only (Select) operation.
Normalized databases are used in DB
testing while demoralized DB is used in data warehouse testing.
There are number of universal
verifications that have to be carried out for any kind of data warehouse
testing. Below is the list of objects that are treated as essential for
validation in ETL testing:
- Verify that data transformation from source to destination works as expected
- Verify that expected data is added in target system
- Verify that all DB fields and field data is loaded without any truncation
- Verify data checksum for record count match
- Verify that for rejected data proper error logs are generated with all
details
- Verify NULL value fields
- Verify that duplicate data is not loaded
- Verify data integrity
ETL Testing Challenges:
ETL testing is quite different from
conventional testing. There are many challenges we faced while performing data
warehouse testing. Here is the list of few ETL testing challenges I experienced
on my project:
- Incompatible and duplicate data.
- Loss of data during ETL process.
- Unavailability of inclusive test bed.
- Testers have no privileges to execute ETL jobs by their own.
- Volume and complexity of data is very huge.
- Fault in business process and procedures.
- Trouble acquiring and building test data.
- Missing business flow information.
Data is important for businesses to
make the critical business decisions. ETL testing plays a significant role
validating and ensuring that the business information is exact, consistent and
reliable. Also, it minimizes hazard of data loss in production.
Hope these tips will help ensure
your ETL process is accurate and the data warehouse build by this is a
competitive advantage for your business.
Moreover, ETL or Data warehouse testing is categorized
into four different areas irrespective of
technology or ETL tools used:
New Data Warehouse Testing – New DW is built and verified from scratch. Data
input is taken from customer requirements and different data sources and new
data warehouse is build and verified with the help of ETL tools.
Migration Testing –
In this type of project customer will have an existing DW and ETL performing
the job but they are looking to bag new tool in order to improve efficiency.
Change Request –
In this type of project new data is added from different sources to an existing
DW. Also, there might be a condition where customer needs to change their
existing business rule or they might integrate the new rule.
Report Testing –
Report are the end result of any Data Warehouse and the basic propose for which
DW is build. Report must be tested by validating layout, data in the report and
calculation.
Why do organizations
need Data Warehouse?
Organizations with organized IT practices are looking
forward to create a next level of technology transformation. They are now trying
to make themselves much more operational with easy-to-interoperate data. Having
said that data is most important part of any organization, it may be everyday
data or historical data. Data is backbone of any report and reports are the
baseline on which all the vital management decisions are taken.
Most of the companies are taking a
step forward for constructing their data warehouse to store and monitor real
time data as well as historical data. Crafting an efficient data warehouse is
not an easy job. Many organizations have distributed departments with different
applications running on distributed technology. ETL tool is employed in order
to make a flawless integration between different data sources from different
departments. ETL tool will work as an integrator, extracting data from
different sources; transforming it in preferred format based on the business
transformation rules and loading it in cohesive DB known are Data Warehouse.
What is a staging
area?
Do we need it? What is the purpose of a staging
area?
Staging area is place where you hold
temporary tables on data warehouse server. Staging tables are connected to work
area or fact tables. We basically need staging area to hold the data, and
perform data cleansing and merging, before loading the data into warehouse.
An ETL (Extract Transform Load) process is all about moving
a variety of data from Source System to the destination Data Warehouse System
by taking data through a number of extraction, transformation, data cleansing
& data validation processes.
Just imagine how easy it will get
for someone as an ETL developer if he gets a chance to visualize all the
transformations & business rules up front in an easy to interpret format.
This is where mapping sheets come into picture.
A carefully designed mapping sheet
up-front can save a lot of pain as handling mapping information increasingly
gets difficult as application grows with time. Only downside of using them is
it takes good effort to create them & then keeping them up-to-date. But,
trust me, rewards of using them easily outnumber the pain of not maintaining
one as the system grows overtime
Each data migration project uses
mapping sheets in one form or the other but the one which I have used too often
& has worked exceptionally well for me is what I am detailing in this here.
To start with a sample Mapping Sheet
would look something like this for any given entity as represented in Figure 1. The sheet can be extended
further by using multiple sheets in the Excel workbook to represent other
entities of the system.
Fig 1 – Sample Mapping Sheet structure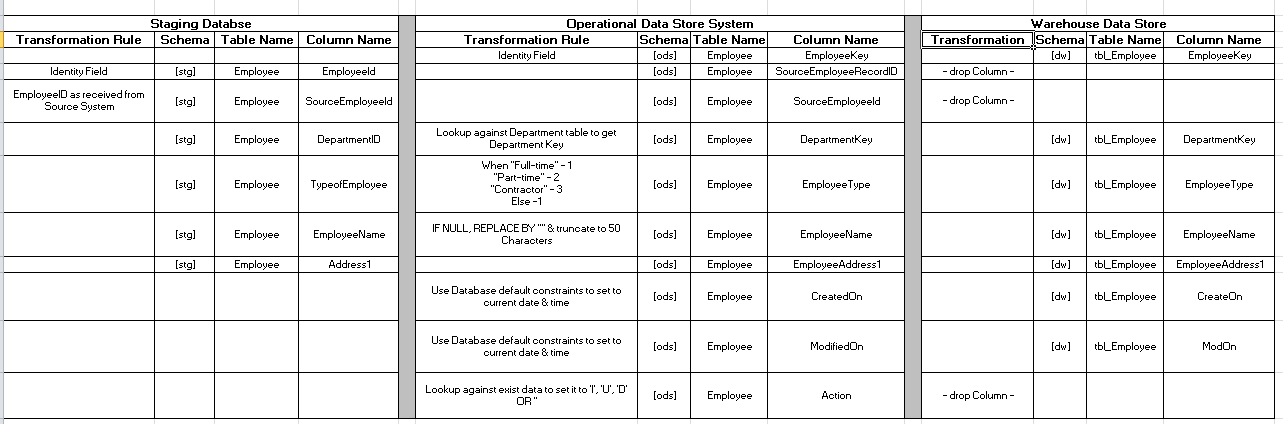
Generally, the extreme left of the
sheet represents data from the Source System or the staging area. The middle
layer represents data validation, data verification, data cleansing &
business rule validation with a number of data-centric transformation rules in
place. There can be more than 1 transformation layer in the centre depending
upon how complex the ETL process is. The extreme right mostly represent Data
Warehouse system.
In the Figure 2 below, I have taken example of Employee table in
staging area to represent how actual table structure from database gets
represented in a mapping sheet.
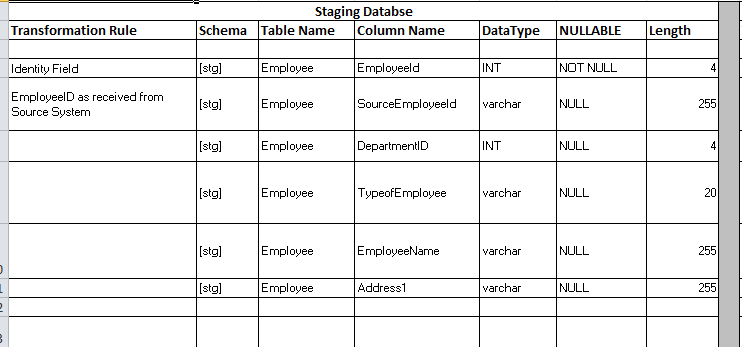
Carefully looking at the snapshot in
figure 2, it provides almost all the information related to a table in a
database. The information includes everything like - Schema name (stg), Name of
the Table [Employee] along with name of the columns, data types & whether
they allows NULL or NOT NULLS values. For eg - EmployeeID is INT & NOT NULL
whereas EmployeeName is going to be varchar(255) NULL column.
On a similar line, mapping sheets
can be extended to further represent structure of the given tables across
different layers. Figure 3 below further
helps you visualize how a field gets mapped, validated & transformed
through different layers of the ETL process while being migrated from Source
System to ODS to DW.
Fig 3 – Transformation rules at the table/field level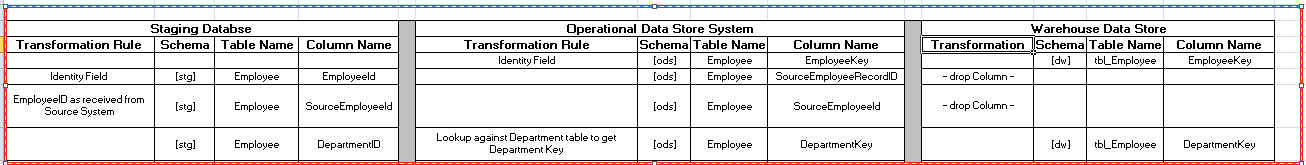
Another efficient use of mapping
sheet would be to documnt Business rules in layman’s term against respective
field right next to them. Please refer to Figure 4 below. The
figure represents only a selective few & a very basic level transformation
rules. Please
note, the transformation rules represented here are only from informative
purpose & real time transformation could vary considerably depending upon
project requirements. The mapping sheets only works as placeholders to
store transformation information.
Some of the sample business rules could be like
1. Use database defaults
to set to Current Date & Time for CreatedOn, ModifiedOn fields.
2. Use SQL Case statement
to set a field to an integer value in warehouse depending upon text information
coming in from source feed.
3. Placeholder to store I, U, D flags in ODS layer to perform
respective actions in warehouse for a given entity – just to name a few
4. Other transformations would be something like these -
Figure 4 – Sample Transformation Rules :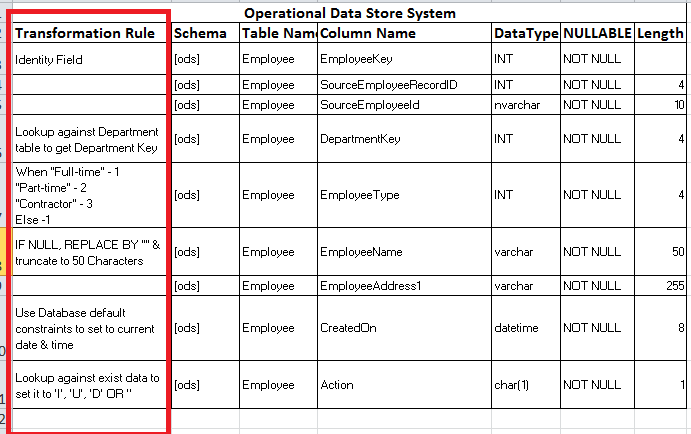
Some of the key points that must be considered while
designing a mapping information document:
1
Design staging area with minimal constraints/indexes and with no or minimum
data integrity checks in place. Consideration for Extraction process must be to
load data from Source System as quickly as possible with minimal data leakage.
Ideally, data type in this layer should be minimally restrictive to allow full
data to pass through to staging area without any data loss. Like allowing
NULLs, data size sufficiently big enough to hold data from feeding source
system.
2 Operational Data Store Layer - In
this layer most of the business rules are defined and data types are generally
tightly coupled with data types in warehouse layer. Most of the data
transformations, error handling & data filtering are done in this layer. An
ideal ODS layer should be able to maintain audit trail information to keep
track of I, U, D operations to Data Warehouse. In this example, “Action"
field in ods.Employee table can be used to maintain current state of a record
throughout the life cycle of ETL process.
3
Data warehouse Layer - This layer contains only current version of data. The
records normally gets Inserted, Updated & Deleted in Data Warehouse
depending upon incoming “Action” field from ODS source. Normally, only
selective few transformation are performed in this layer, the ones which are
specific to data available in data warehouse
With this, I will now sign off on
this topic. I have tried keeping this information in its basic & simplest
form so I hope this information will come handy in your respective projects.
Please do share your inputs, feedback & comments & I will be more
than happy to amend/improve this posting further.
Decoding Part Copied and Reference:
- www.msbigeek.com













